With the application of information technologies such as cloud computing, big data, Internet of Things, and digital transformation, the global data center market continues to expand, reaching US$82.2 billion (10.04%) in 2023 and is expected to reach US$96.8 billion in 2025. China’s market size has grown significantly, with about 240.7 billion yuan (26.68%) in 2023 and is expected to exceed 318 billion yuan in 2025.
1. The energy consumption dilemma in the era of high computing power
Driven by technology, data centers are evolving from traditional storage to “computing power supermarkets”, supporting diverse scenarios such as AI training and blockchain verification by deploying heterogeneous computing facilities such as GPU clusters and quantum computing nodes. While this transformation meets the explosive demand for computing power, it has also led to a surge in data center power consumption, becoming a core challenge for global digital infrastructure.
In 2024, China’s intelligent computing power will reach 725.3EFLOPS, a year-on-year increase of 74.1%, an increase of more than three times that of general computing power (20.6%) in the same period; The market size was US$19 billion, a year-on-year increase of 86.9%. In the next two years, China’s intelligent computing power will continue to grow rapidly. In 2025, China’s intelligent computing power will reach 1,037.3 EFLOPS, an increase of 43% from 2024; In 2026, China’s intelligent computing power will reach 1,460.3 EFLOPS, double that of 2024.
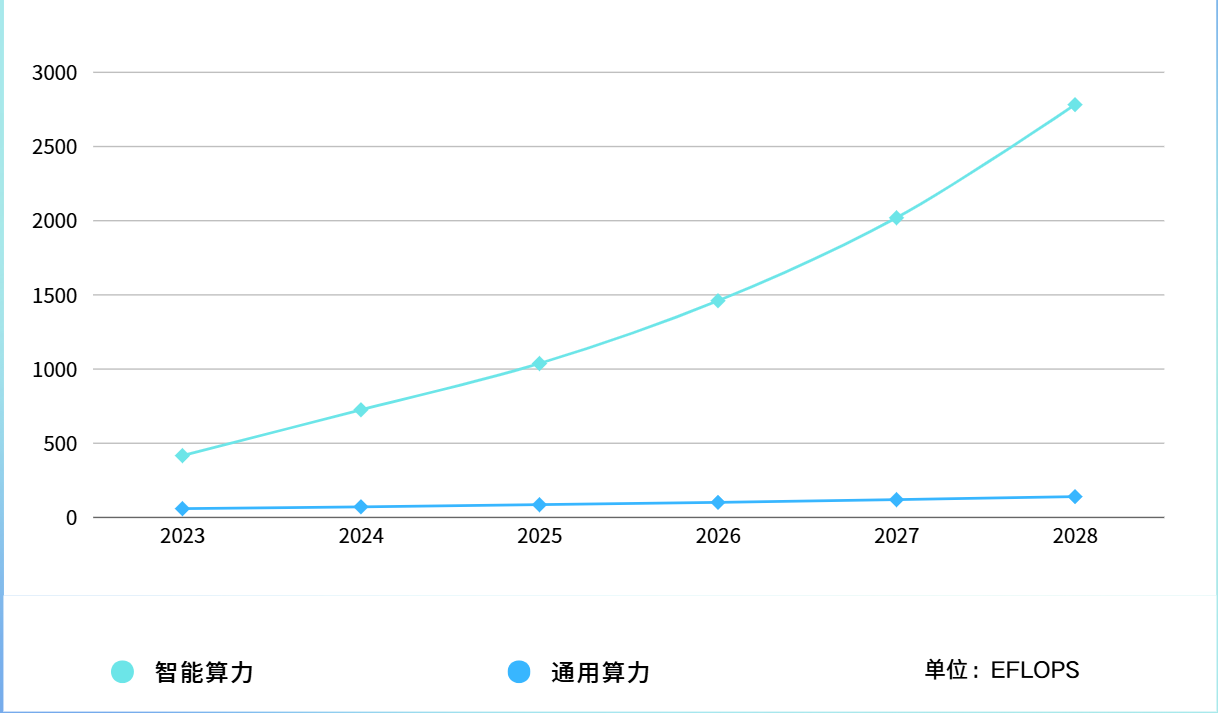
Figure The scale and forecast of China’s intelligent computing power and general computing power (compiled by HFC based on public information)
The heat dissipation crisis under the surge in computing power
The physical characteristics of the chip determine that the increase in computing power will inevitably be accompanied by a surge in thermal energy output. As processor performance increases, power consumption (P) increases in square orders (P ≈ C×V²×f), and the vast majority of power consumption is eventually converted into heat. Whether it’s high-performance computing, AI training, or cryptocurrency mining, every leap in computing power comes with more severe cooling challenges.
2. The triple cooling challenge of data centers
Breakthrough in technical limits
The computing power of chips has soared, the air-cooled heat dissipation efficiency has reached the physical limit, and the high temperature has led to a decrease in chip performance and a shortened device life.
Safety and reliability crisis
For every 10°C increase in temperature, the failure rate of electronic components increases by 50%;The existing temperature control system has a response delay of 3-5 seconds, and emergency cooling switching creates a blind spot to protect it.
Energy efficiency and economic game
Global PUE regulation is becoming stricter (EU requirement < 1.3, China East and West computing requirement < 1.25);Liquid cooling technology can reduce PUE to less than 1.1, but the initial investment increases.
3. Thermal interface materials: the core hub of the heat dissipation system in the era of high computing power
In the process of data center evolution to high computing power, solving the heat dissipation problem of high-performance processors directly determines the improvement of server productivity.
Although liquid cooling technology is gradually replacing air cooling, it brings more efficient cooling solutions to data centers. However, the key role that really lurks “under the chip” and determines heat dissipation efficiency – thermal interface materials (TIMs) are often overlooked.
The performance of thermal interface materials directly determines that more than 60% of the interfacial thermal resistance in cold plate liquid cooling becomes the key bottleneck for heat transfer from the chip to the cold plate; The long-term stability of materials and dielectric fluids in immersion liquid cooling affects the reliability and maintenance cost of the system. In the context of the continuous increase in computing power density, optimizing the performance of TIMs has become a key breakthrough in improving the energy efficiency and reliability of data centers.
4. High-density computing power data center, HFC graphene thermal conductivity gasket innovative heat dissipation solution
With the increasing performance requirements of TIM (Thermal Interface Material) for cold plate and immersion liquid cooling in data centers, graphene thermal gaskets are a promising and innovative solution due to their unique material properties. How does HFC longitudinal graphene thermal gasket break through the key heat dissipation bottleneck of the data center liquid cooling system?
Figure HFC longitudinal graphene thermal conductivity gasket
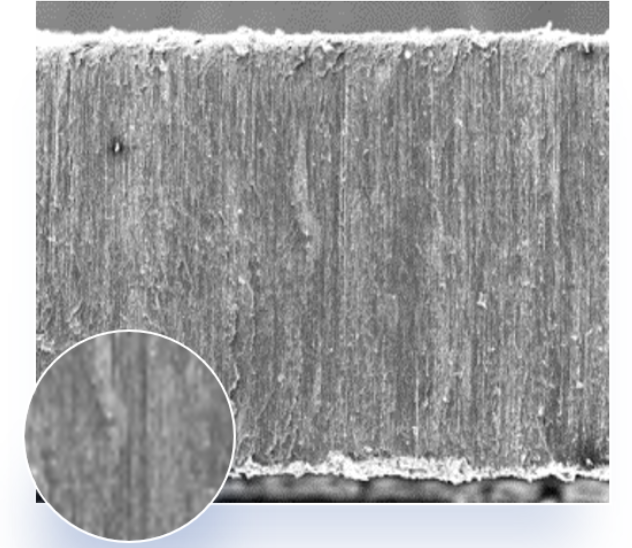
Figure Hfc graphene thermal conductivity gasket is composed of longitudinal continuous, high thermal conductivity, and low density graphene
1. Interface thermal resistance optimization: build an efficient heat conduction pathway
The continuous heat conduction path is constructed by orientation arrangement technology, and the thermal conductivity is improved by more than 10 times compared with conventional thermal interface materials. At the same time, relying on the orientation process and the appropriate packaging pressure, the thermal resistance is as low as 0.04°C·cm²/W. Through the ultra-thin process, it can be matched with up to 70% of the compression volume, and the BLT in the TIM scenario of chip packaging can reach 0.1mm, shortening the heat conduction path and further reducing the overall thermal resistance.
2. Material aging protection: strengthen weather resistance and stability
Porous structure design for precise interface deformation. The internal porous structure quickly responds to the local deformation of the cold plate/chip surface, eliminating assembly gaps, eliminating the generation of interface voids, and there is no risk of pumping out for long-term use.
Creep resistance: high rebound rate and low compressive stress, maintain a stable fit under cold plate assembly pressure, and avoid the increase in thermal resistance caused by stress relaxation.
High reliability: It has passed the rigorous 1000h high temperature, high and low temperature impact, and double 85 aging tests of HFC’s internal CNAS accreditation laboratory and mass production customer laboratory, respectively, to meet the 7×24-hour operation needs of the data center.
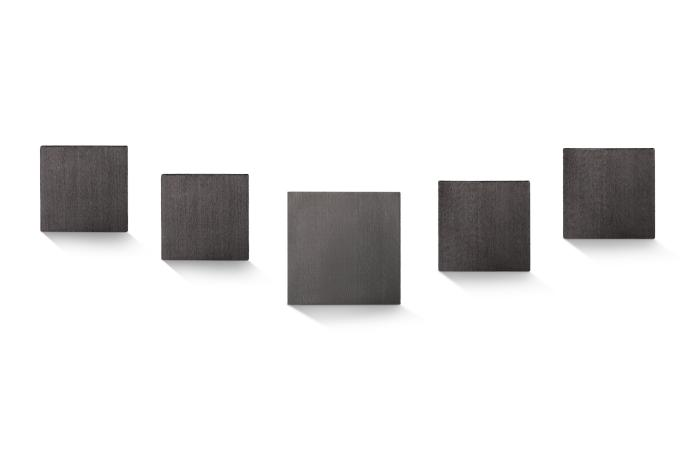
Figure HFC longitudinal graphene thermal conductivity gasket
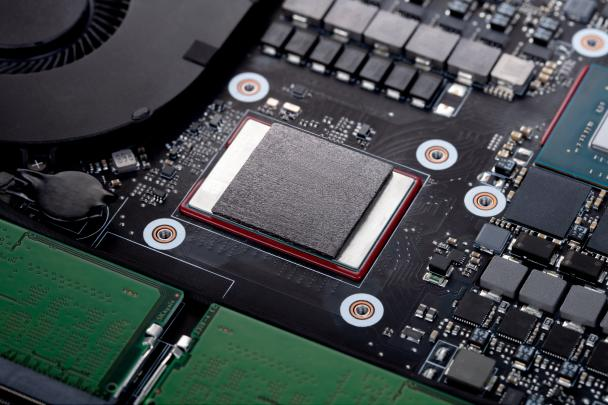
Figure HFC longitudinal graphene thermal conductivity gasket
3. Mechanical performance enhancement: adapt to pressure and impact scenarios
Low-stress assembly, protect high-precision chips, high rebound rate adapts to CPU/GPU and other sensitive chips, reducing the risk of microcracks caused by mechanical stress.
4. Full life cycle cost advantage
Large-scale production reduces costs and high-quality mass commercial use. HFC longitudinal graphene thermal conductive gasket has accumulated many years of experience in chip heat dissipation applications, and has achieved automated production lines and mass production delivery, and its product quality has been recognized by many leading enterprises in the chip industry at home and abroad and won the “Quality Excellence Award”.
Cold plate type: The graphene thermal conductive gasket process is simple, which can realize automatic placement without complicated processes, greatly saving packaging time and equipment investment costs.
Immersion type: long-life design, will not be pumped out or material migration due to high temperature like silicone grease and phase change materials, suitable for large-scale scenarios such as data center heat dissipation.
5. Improved process compatibility to meet the needs of diverse scenarios
Adaptation to the surface roughness of the cold plate: With high compression rebound, it can cover the processing accuracy of the mainstream cold plate, and the contact thermal resistance control ability is better than that of traditional thermal conductive materials.
Dielectric fluid compatibility: Graphene sheets are chemically inert and do not react with fluoride liquids and mineral oils. It can meet the long-term immersion needs of fluorinated liquid and mineral oil, and its chemical stability is better than that of traditional materials.
